Prostate enlargement, medically known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition affecting millions of men, particularly as they age. BPH can lead to uncomfortable symptoms, including frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty emptying the bladder. While traditional treatments such as medication and surgery have been the mainstay for managing BPH, a newer, minimally invasive procedure called Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) has emerged as an effective alternative. This article will explore the science behind PAE, its benefits, and what patients can expect from the procedure.
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Before delving into PAE, it’s essential to understand BPH and its implications. The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder, responsible for producing seminal fluid. As men age, hormonal changes can cause the prostate to enlarge, pressing against the urethra and obstructing urine flow.
Symptoms of BPH
Men suffering from BPH may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination: Increased urge to urinate, especially at night (nocturia).
- Weak urine stream: Difficulty starting or maintaining urine flow.
- Incomplete bladder emptying: A feeling of not fully emptying the bladder after urination.
- Urgency: A sudden, strong need to urinate.
These symptoms can significantly impact a man’s quality of life, leading to sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even depression.
Traditional Treatments for BPH
The management of BPH has typically involved a range of treatments, from lifestyle modifications to medications and surgical interventions.
Medications
Common medications include:
- Alpha-blockers: These relax the muscles around the prostate and bladder neck, improving urine flow.
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors: These help shrink the prostate by blocking the hormone responsible for prostate growth.
While effective, these medications can have side effects, and not all patients find relief.
Surgical Options
For men who do not respond to medications, surgery may be recommended. Common surgical procedures include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): A surgical procedure that removes excess prostate tissue through the urethra.
- Laser therapy: Uses lasers to remove or destroy excess prostate tissue.
While surgery can provide significant relief, it comes with risks, including bleeding, infection, and sexual dysfunction.
What is Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)?
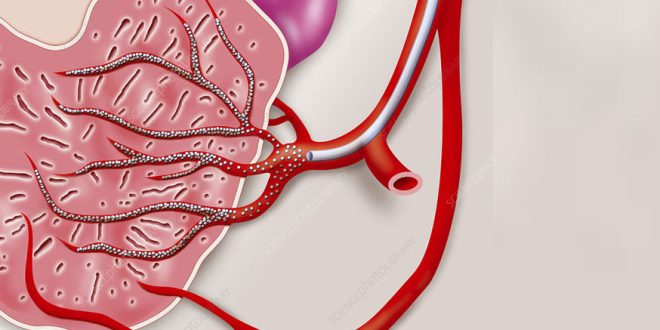
Prostate Artery Embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that targets the blood vessels supplying the prostate. By reducing blood flow to the enlarged prostate, PAE aims to shrink the gland and alleviate symptoms without the need for traditional surgery.
How Does PAE Work?
- Diagnosis and Preparation: Before the procedure, patients undergo imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, to assess the prostate and identify the arteries involved.
- Catheter Insertion: During the procedure, an interventional radiologist inserts a thin catheter into the femoral artery (in the groin) or the radial artery (in the wrist) and navigates it to the prostate arteries using real-time imaging.
- Embolization: Once in place, the physician injects tiny particles through the catheter into the prostate arteries. These particles block blood flow to the prostate, reducing its size over time.
- Recovery: Patients typically experience a short recovery period, often leaving the outpatient facility the same day.
Benefits of Prostate Artery Embolization
PAE offers several advantages over traditional treatments for BPH:
1. Minimally Invasive
As a minimally invasive procedure, PAE requires only small incisions and typically involves local anesthesia. This results in less pain, reduced scarring, and a shorter recovery time compared to surgical options.
2. Outpatient Procedure
PAE is usually performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to go home the same day without the need for an overnight hospital stay.
3. Reduced Risks
With lower risks of complications such as bleeding and infection, PAE is often seen as a safer alternative to surgical options.
4. Preserved Sexual Function
Many men worry about the potential for sexual dysfunction after traditional BPH surgeries. PAE has a lower risk of affecting sexual function, making it an attractive option for many patients.
5. Effective Symptom Relief
Studies have shown that PAE can effectively reduce BPH symptoms and improve urinary flow, providing patients with significant relief.
Who is a Candidate for PAE?
While PAE is an effective treatment for many men with BPH, it may not be suitable for everyone. Ideal candidates typically include:
- Men with moderate to severe BPH symptoms that significantly affect their quality of life.
- Patients who have not found relief from medications.
- Individuals seeking a minimally invasive treatment option with a reduced risk of complications.
A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider specializing in BPH is crucial to determine if PAE is the right choice.
What to Expect Before, During, and After PAE
Before the Procedure
- Consultation: A thorough evaluation and discussion with an interventional radiologist will cover medical history, symptoms, and treatment options.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans may be ordered to assess prostate size and blood supply.
- Pre-Procedure Instructions: Patients may need to stop taking certain medications, particularly blood thinners, in the days leading up to the procedure.
During the Procedure
- Anesthesia: Patients receive local anesthesia and sedation to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Catheterization: The physician will insert a catheter into the appropriate artery and navigate to the prostate arteries using imaging guidance.
- Embolization: Tiny particles are injected to block blood flow to the prostate, leading to its eventual shrinkage.
After the Procedure
- Recovery: Patients are monitored for a short time before being discharged. Some discomfort or mild bruising at the catheter site is normal.
- Post-Procedure Care: Instructions will be provided regarding activity levels, hydration, and medications to manage any discomfort.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Patients will have follow-up visits to assess symptom improvement and monitor recovery. Symptom relief can take several weeks to months as the prostate shrinks.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While PAE is generally safe, it is essential to understand the potential risks and complications:
- Post-Embolization Syndrome: Some patients may experience flu-like symptoms, including pelvic pain, fever, and fatigue, in the days following the procedure. This typically resolves within a week.
- Infection: As with any medical procedure, there is a small risk of infection at the catheter insertion site.
- Urinary Complications: Rarely, patients may experience urinary retention or worsening symptoms immediately following the procedure. In most cases, this resolves as healing occurs.
- Allergic Reactions: Patients may have allergic reactions to contrast dye used during the imaging process. This is typically managed promptly.
Discussing these risks with a healthcare provider will help patients make informed decisions.
Long-Term Outcomes of PAE
Research indicates that PAE can provide long-lasting relief from BPH symptoms. Studies show significant improvements in urinary function and quality of life for many patients.
Effectiveness of PAE
- Symptom Relief: Clinical studies have shown that over 80% of patients experience a reduction in urinary symptoms after PAE.
- Prostate Size Reduction: On average, patients see a decrease in prostate size by 30-50% within six months of the procedure.
- Quality of Life Improvements: Many men report improved quality of life, including better sleep and the ability to engage in daily activities without the burden of frequent urination.
Conclusion: A New Hope for Men with BPH
Prostate Artery Embolization is an exciting advancement in the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. As a minimally invasive solution, PAE offers hope for men seeking relief from the uncomfortable symptoms of prostate enlargement. With benefits such as lower risks, preserved sexual function, and effective symptom management, PAE has established itself as a viable alternative to traditional BPH treatments.
Men experiencing symptoms of BPH should consult with their healthcare provider to discuss their options and determine if PAE is the right choice for them. With the right treatment plan, many men can regain control of their urinary health and enjoy a better quality of life.
 Diverse Perspectives: Insights & Stories Exploring Ideas, Sharing Knowledge
Diverse Perspectives: Insights & Stories Exploring Ideas, Sharing Knowledge