Kidney disease often goes undetected in its early stages because symptoms can be subtle or mistaken for other health issues. One of the earliest signs is changes in urination patterns, such as increased or decreased frequency, foamy or bloody urine, or discomfort during urination. Swelling, particularly in the hands, feet, or around the eyes, can also signal kidney problems. This occurs because damaged kidneys struggle to remove excess fluids and waste from the body, causing fluid retention.
As kidney function continues to decline, additional symptoms can emerge. Persistent fatigue, for example, is common because the kidneys help produce a hormone called erythropoietin, which is involved in red blood cell production. When kidneys are impaired, lower levels of red blood cells can lead to anemia, resulting in tiredness and weakness. Shortness of breath, nausea, and difficulty concentrating can also be symptoms, as waste buildup in the bloodstream affects overall health.
In more advanced stages, kidney disease may lead to more noticeable symptoms, such as muscle cramps, especially in the legs, dry and itchy skin, and an ongoing metallic taste in the mouth. High blood pressure is both a cause and symptom of kidney disease, as poorly functioning kidneys struggle to regulate blood pressure. If any of these symptoms appear.
10 Signs Of Kidney Disease
Here are ten common signs and symptoms of kidney disease to look out for:
Fatigue
Kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and balancing electrolytes, and they also help produce a hormone called erythropoietin, which supports red blood cell production. When kidney function declines, waste builds up in the bloodstream, and fewer red blood cells are produced, leading to anemia. This reduced oxygen delivery to tissues results in feelings of fatigue, weakness, and decreased energy. Many people with kidney disease report exhaustion even with enough rest and may struggle with daily activities.
Swelling (Edema)
When kidneys can’t remove excess sodium and fluid, it leads to fluid retention, causing swelling, also known as edema. This swelling is often most noticeable in the legs, ankles, feet, and sometimes the hands or face. The fluid buildup can also affect internal organs, leading to discomfort and, in severe cases, complications with other bodily functions. Swelling may be painful and can worsen throughout the day due to prolonged standing or sitting.
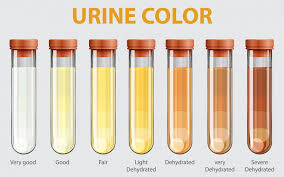
Changes in Urination
Kidney disease frequently leads to noticeable changes in urination. Symptoms include increased or decreased frequency of urination, foamy or bubbly urine (indicating protein leakage), and sometimes blood in the urine. These changes can also include discomfort or pain while urinating, especially if infections are present. Any persistent or significant change in urination patterns warrants medical attention, as early detection of kidney issues can slow progression.
Shortness of Breath
The kidneys help regulate fluid levels, and in kidney disease, excess fluid may accumulate in the lungs, causing shortness of breath. Additionally, anemia from reduced red blood cell production further limits oxygen delivery to tissues. People with advanced kidney disease may experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity, and sometimes even while lying down, as fluid may settle in the lungs, intensifying the problem.
High Blood Pressure
Kidneys are essential for maintaining blood pressure, and kidney disease can disrupt this balance. Damaged kidneys may struggle to remove excess salt and fluid, leading to increased blood volume, which raises blood pressure. Additionally, kidney disease can lead to changes in the hormone system that regulates blood pressure, causing hypertension. High blood pressure also accelerates kidney damage, creating a dangerous cycle that can lead to further health complications if left unmanaged.
Loss of Appetite
A reduced desire to eat is a common sign of kidney disease and can be attributed to a buildup of toxins in the blood, which affects digestive function. The result can be nausea, vomiting, and an overall loss of appetite, sometimes leading to unintended weight loss and malnutrition. This symptom is particularly concerning as poor nutrition can further weaken the body and increase the risk of infections, compounding the effects of kidney disease.
Metallic Taste in Mouth
Kidney disease can cause a metallic taste in the mouth or a persistent sense of a “foul” or “ammonia-like” breath odor. This results from uremia, a buildup of waste products that would normally be filtered out by healthy kidneys. This taste disturbance often diminishes enjoyment of food and can reduce appetite. In some cases, patients may avoid certain foods altogether, which can lead to further nutritional deficiencies.
Muscle Cramps
Imbalances in electrolytes, like calcium and phosphorus, are common in kidney disease, leading to frequent muscle cramps. Magnesium and potassium levels, which play a role in muscle contraction, may also be affected, worsening cramps and causing painful muscle spasms, especially in the legs. This discomfort can interfere with sleep and may even limit physical activity, impacting quality of life.
Difficulty Concentrating
Cognitive issues such as memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, and mental fog are common in people with kidney disease. These symptoms are often due to a combination of anemia, reduced oxygen supply to the brain, and toxin buildup. As kidney disease progresses, these cognitive effects may become more pronounced, leading to problems with work, relationships, and daily activities. Addressing anemia and managing kidney function can help alleviate some of these cognitive symptoms.
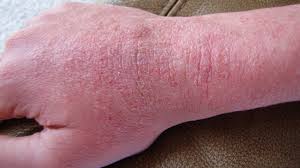
Dry and Itchy Skin
Healthy kidneys maintain the balance of minerals and nutrients and help keep skin hydrated. When kidneys fail to remove excess waste, it can cause a buildup of minerals like phosphorus, leading to dry, itchy skin. This persistent itching can cause significant discomfort and may lead to scratching that damages the skin. In more advanced stages of kidney disease, this itching can be intense and difficult to manage, requiring special care and treatment to relieve symptoms.
Name Of Kidney Disease And Treatment With Natural Remedies
Kidney diseases encompass a variety of conditions, each with unique causes and symptoms. Here’s an overview of common kidney diseases and some natural remedies that may help manage symptoms and support kidney health. If you’re specifically looking for Natural Remedies for Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD), these options are also included below.
1. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Description: CKD is the gradual loss of kidney function, often caused by diabetes, hypertension, or long-term kidney damage.
- Natural Remedies:
- Dandelion Root and Nettle Leaf: Known for their diuretic effects, they help detoxify the body and support kidney function.
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: A diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low in salt and protein can reduce strain on kidneys.
- Hydration: Drinking adequate water helps flush toxins and supports kidney health.
2. Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
- Description: PKD is a genetic disorder characterized by fluid-filled cysts that grow within the kidneys, often leading to kidney enlargement, pain, and impaired kidney function.
- Natural Remedies:
- Curcumin (from Turmeric): Curcumin has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce cyst growth and support kidney function. Consider adding turmeric to meals as a Herbal Treatment for Polycystic Kidney Disease or taking supplements after consulting a healthcare provider.
- Green Tea and Hibiscus Tea: Both contain antioxidants that support blood pressure regulation and reduce oxidative stress, potentially helping with PKD management.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, omega-3s reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health, which is important for PKD patients. Include fatty fish in your diet or consider a fish oil supplement.
3. Kidney Stones
- Description: Hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys, often causing severe pain and potential kidney damage if not treated.
- Natural Remedies:
- Hydration: Drinking 2–3 liters of water daily helps flush out minerals, reducing the risk of stone formation.
- Citrus Fruits: Lemons and oranges contain citrate, which can help prevent the buildup of kidney stones.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Contains acetic acid, which may aid in dissolving smaller stones and alleviating kidney pain.
4. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- Description: A sudden decline in kidney function, often due to injury, infection, or medication side effects.
- Natural Remedies:
- Aloe Vera: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it can support kidney recovery, though use with caution as high doses can cause side effects.
- Adaptogens: Herbs like ashwagandha and ginseng may support stress management, which can help the body recover from AKI.
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing protein and salt intake can alleviate stress on the kidneys, aiding recovery.
5. Glomerulonephritis
- Description: Inflammation of the glomeruli, the kidney’s filtering units, often related to autoimmune diseases.
- Natural Remedies:
- Omega-3s: Found in fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage inflammation in the kidneys.
- Green Tea: High in antioxidants, green tea can reduce inflammation and protect kidney cells.
- Herbs Like Reishi Mushroom: Known for immune-supporting properties, they may help reduce inflammation related to autoimmune conditions.
Conclusion;
Kidney disease often presents subtly, with signs like fatigue, swelling, changes in urination, muscle cramps, and high blood pressure. Early recognition and lifestyle changes can support kidney health alongside medical treatments.
Related Article; Common Health Foods That Might Harm Hormonal Balance
Also Related; The Role of Multivitamins in Women’s Immune System Health
 Diverse Perspectives: Insights & Stories Exploring Ideas, Sharing Knowledge
Diverse Perspectives: Insights & Stories Exploring Ideas, Sharing Knowledge